Income Tax is a tax on income collected by the government to fund infrastructure development, pay salaries, etc. Income Tax is a direct tax like capital gains tax and securities transaction tax etc. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is means through which the government generates steady revenues by levying taxes at sources such as salary or other payments. Additionally, Income Tax is to be paid by every Individual, HUF, AOP, BOI, Firms, and Companies.
Income Tax in India
In India, a direct tax is governed as per Income Tax Act, 1961 along with Income Tax Rules, 1962, Notifications and Circulars issued by Central Board of Direct Taxes. Moreover, Income Tax is levied based on the different types of incomes and taxpayers. Furthermore, there are different categories of taxpayers under the Income Tax Act.
- Individual residents aged below 60 years
- Senior citizen aged between 60 to 80 years
- Super senior citizen aged above 80 years
- Non-residents (NRI)
- Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- Firms / AOP / BOI / Local Authorities / Co-operative Societies
- Company
Income Tax for Resident Individuals
An individual’s income is divided under different income heads such as salary, house property, capital gains, business or profession, and other sources. Income is taxed at slab rates except for a few special rate incomes.
- The majority of individuals have income from salary, house property, and interest which makes them eligible to file ITR-1 (SAHAJ).
- In the case of income from multiple house properties, ITR-2 can be filed.
- Those with income from capital gains (say by way of casual stock trading or sale of the property) can file ITR-3.
- Individuals having income from proprietary business or profession can file ITR-4 (SUGAM) or ITR-3.
- Any Individuals who are partners in a firm and earn income by way of salary, remuneration, interest or profits sharing, can file ITR-3
- Individuals whose turnover from proprietary Business exceed Rs. 2 crores have to get the books of account audited and file ITR-3.
- Similarly, professionals’ gross professional receipts exceed Rs 50 Lakhs have to get the books of accounts audited and file ITR-3.
- For a Resident Indian, global income will be taxable in India i.e income earned in India as well as outside India will be taxable in India. A tax credit will be available if such income is already taxed in a foreign country and India has a treaty with such a foreign country to avoid double taxation.
Income Tax for NRI
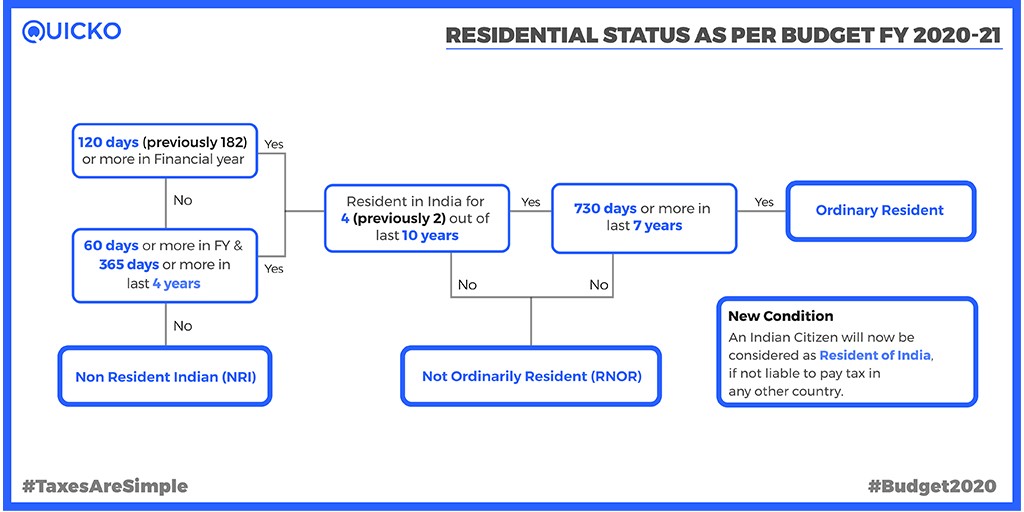
A Non-Resident Indian (NRI) has to file an income tax return in India only if he has earned any income in India. He does not have to disclose his foreign income from the country of residence while filing the tax return.
The type of return forms will be the same as applicable to resident India. While filing the return, NRI can claim the credit if the income earned in India is also taxed in the country of his residence. The basic principle here is that a single income should not be taxed twice. So if income earned in India is taxed in a foreign country as well, then NRI can claim the credit of the taxed paid in a foreign country while filing return in India. Credit will be allowed only if India has an agreement to avoid double taxation with a foreign country.
Income Tax for HUF (Hindu Undivided Family)
Income Tax Act recognizes Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) as a separate legal entity from its members. It has a unique PAN which if different from its Karta and members. HUF also enjoys a basic exemption limit of Rs. 2,50,000 just like the individuals.
- HUFs have to file their Income Tax Return separately
- Incomes earned out of assets in the common pool of HUF or any business activities run in the name of HUF are to be included in a tax return.
- HUF can have income from all sources, except for salary.
- Income will be taxed at slab rates applicable to individuals
- HUF can file a return in ITR-2, ITR-3, and ITR-4
- Just like individuals, if HUF is carrying business and turnover exceeds Rs. 2 crores then books of account have to be audited and ITR-4 is to be filed.
Income Tax for Partnership Firms
Partnership firm / LLP is a separate legal entity, independent from its partners. It has its own PAN.
- Partnership firms / LLPs have to file an income tax return in ITR-5
- Income from business or profession, house property, capital gains and other sources can be filed in ITR-5
- The tax will be applied at a flat rate of 30% on a firm’s income.
- The firm’s profits (after payment of tax) which are distributed amongst partners are tax-free in the hands of the partners.
- However, any salary, remuneration or interest paid to partners will be taxable in the hands of the partner. And a firm can claim the same as an expense from its income.
Income Tax for Companies
Companies have a separate legal identity and a unique PAN. In India, there are Domestic Companies and Foreign Companies.
- Companies have to file an income tax return in ITR-6
- It is mandatory for companies to file an income tax return and provide details of the Statutory Audit in the return.
- If turnover from business exceeds Rs. 2 crores, then companies have to carry of Tax Audit as per Income Tax Act and provide the details of the same in Income Tax Return.
- Companies can have income from the business, house property, capital gains and other sources.
- However, companies claiming an exemption under section 11 of the income tax act will be called trusts and they have to file return in ITR-7
- The income of Domestic company is taxed at a flat rate of 30% whereas the income of Foreign company is taxed at a flat rate of 40%
FAQs
An income tax return is a form used to report income and file taxes with tax authorities such as the Income Tax Department (ITD) in India. Commonly known as ITR, tax return allows the taxpayer to calculate his/her tax liability and pay dues or request refunds. There are different prescribed ITR forms in India depending on one’s income situation.
Income Tax can be calculated by applying slab rates on taxable income, which is the addition of all the gross incomes such as salary, rent, business or profession, minus Chapter VI A deductions such as Provident Fund, Life Insurance Premium, ELSS, NSC, Medical Insurance Premium, etc.
It is mandatory to file the Income Tax Returns (ITR) online for all the registered taxpayers whose taxable income. However, paper returns can be filed by those who are above 80 years of age and do not have any income from regular business or profession.

